SustAInability: doing good faster, better
What do AI and sustainability have in common? More than you might think! There's some real common ground: both rely on technology and innovation to thrive. What if we apply the potential of AI to the urgent issues we need to address in sustainability? We arrive at the AI for good concept .
AI can help accelerate sustainability and the energy transition, especially in sectors such as agriculture, energy, transport or water usage, where it can bring positive disruption. As an enabler of big data analytics, AI could be a tool for managing risk and identifying investment opportunities that drive financial returns while optimizing environmental and social impact.
Nevertheless, AI faces significant sustainability challenges. Current AI technology makes intensive use of power and other scarce resources such as water.
As the world enters the Intelligent Age - a term coined by the World Economic Forum for our era of rapid technological advancement- change and transformation can accelerate sustainable and social progress, but how fast and at what cost?.
The potential of AI lies in its ability to make use of data, optimize processes, foster innovation and build resilience. AI-based models are particularly good at capturing complex, non-linear relationships that make a difficult fit with traditional ones.
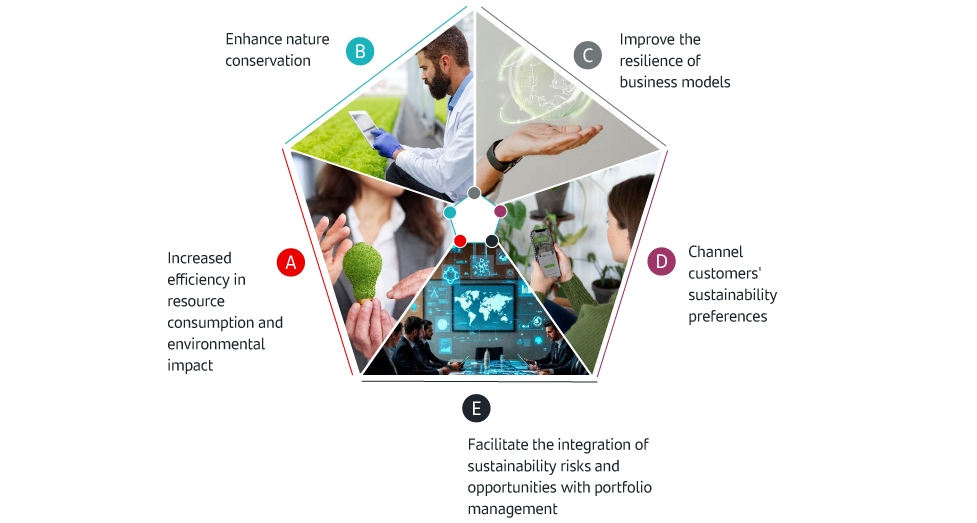
Use cases of AI for environmental impact
A. Increased efficiency in resource consumption and environmental impact
AI can help companies identify and i mplement sustainability improvements within operations and along the supply chain. Modelling the functioning of physical assets, factories, buildings, roads or electric grids using digital twins will better inform decision making and reduce consumption of materials, energy, and water.
B. Enhance nature conservation
AI-powered systems can monitor ecosystems , wildlife habitats and natural resources more efficiently than existing methods, enhancing conservation and preservation and sustainable resource management.
Fighting against wildfires , protecting natural ecosystems and preserving wildlife through bioacoustics (leveraging AI to process audio recordings of diverse species for wildlife population assessment) are other innovative opportunities.
C. Improve the resilience of business models
AI-powered tools are valuable instruments for analyzing vast datasets to identify climate risks (exposure of facilities to weather events) and developing mitigation and transition plans for the most endangered locations.
D. Channel customers' sustainability preferences
AI can help customers make more informed purchasing decisions regarding the sustainability of products and services. For instance, an AI-driven recommendation engine that can tailor product suggestions with consumers´ sustainability preferences.
E. Facilitate the integration of sustainability risks and opportunities with portfolio management
AI technologies enable in-depth analysis of large sets of unstructured data from many different sources, which helps in identifying parameters and hidden dynamics, trends, and patterns; gaps can be filled by sourcing alternative data. Moreover, AI can allow dynamic portfolio optimization for sustainability criteria and goals when connected to real time data.
SustAInability by sectors. Who can benefit the most?
The use of AI can contribute to the energy transition and support adaptation and resilience in the following sectors:
Healthcare and Genetics
Personalized medicine and genomics enabling tailored treatments could produce better health outcomes at lower cost for more people.
Utilities and renewables
Improve the prediction of weather conditions to manage supply and demand and optimize energy storage. It can mitigate negative impacts from renewable infrastructure.
Agriculture
Precision agriculture can help ensure food security by optimizing crop yields, soil health monitoring, and water usage, boosting agricultural production.
Transport and smart cities
Along with autonomous transport including trucking , more accurate traffic prediction can lead to reduce carbon footprints.
The expected impact in numbers
Using AI for environmental applications could:
- Reduce global greenhouse gas emissions (GHG). According to BCG , AI could help mitigate 5% to 10% of GHG emissions by 2030.
- Create jobs on a net basis. The WEF estimates that AI could generate 7% net growth in global jobs in 5 years.
- Boost global GDP by 3.1 – 4.4% (up to USD 5.2tr)
- Boosting the social economy , where AI could add between $182 - $308 billion in value annualy to this sector.
Challenges
- Resource intensity. This will reduce AI power intensity, as happened with the rise of power demand from expansion of data centers earlier in the century, which was later offset by the use of cloud services .
- Data availability. The main hurdle to train AI models to drive sustainability outcomes is data , that needs to be public, of high quality and available for model validation via Sandbox.
- Ensure a “fair AI for all”. By analogy to the Just transition in sustainability, AI should ensure fair adoption , leaving no one behind.
- Regulation and collaboration. AI needs to be supported by the necessary regulatory insight and oversight to avoid significant gaps in transparency, safety, and ethical standards.
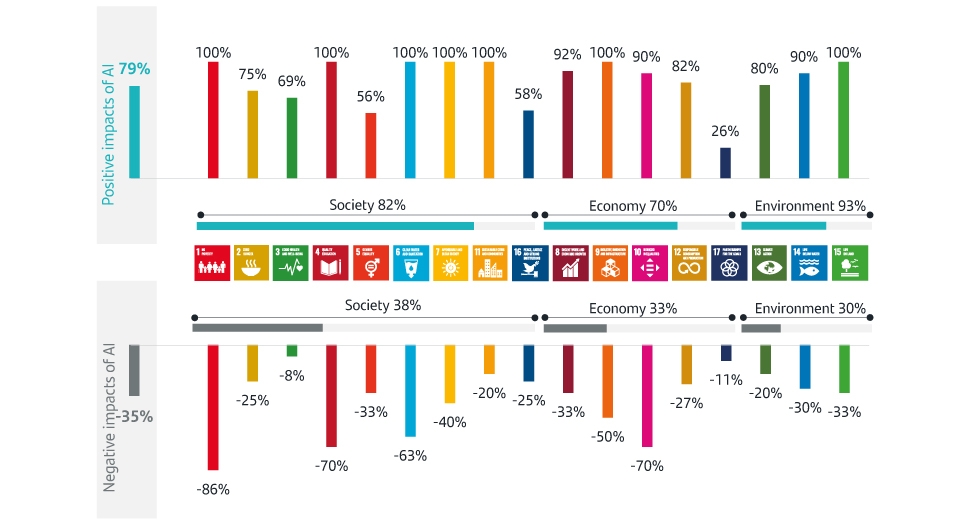
Impacts of AI on the SDGs
Source: Nature
And what about social areas?


Mental Health

Disability Inclusion

Healthcare

Social Entrepreneurship

Humanitarian aid
AI has the potential to become a net creator of jobs and an economic booster. It may also contribute to tackle challenges related to climate change and nature-based risks.
AI can offer many possibilities for governments and companies and highly beneficial applications for sustainability and social projects where it can be disruptive, unfolding attractive investing opportunities. Sectors such as infrastructure, water management or agritech could be some of the themes that may be less exposed to policy changes towards sustainability.
At present, AI still faces significant challenges, such as resource consumption, data requirements, biases and the need for regulation, despite at this stage it is too early to make any predictions about negative effects, as the technology is still evolving towards improved efficiency.
- ITU, AI for good: Aboutus - AI for Good
- PwC: How AI can enable a sustainable future
- Fide: AI Revolution: expandingthereach and impactofsustainableinvestment - Oxford/24 Report - Fundacion Fide
- MIT: AI isanenergyhog. Thisiswhat it meansforclimatechange. | MIT TechnologyReview
- Forbes: AI IsAcceleratingtheLossofOurScarcest Natural Resource: Water
- WEF: TheIntelligent Age: A time forcooperation | WorldEconomicForum
- KPMG: The Use of AI in SustainableFinance
- WEF: Digital twinswillchangethefaceof industrial ecosystems | WorldEconomicForum
- UN: 5 Insightsinto AI as a Double-EdgedSword in ClimateAction | UnitedNationsUniversity
- Los Angeles Times: After L.A. fires, thesearchforbettertoolstofightblazespicks up - Los Angeles Times
- Microsoft: Bioacoustics - Microsoft Research
- Bain & company AI and Sustainability: ThePowerofIntegration | Bain & Company
- CFA institute: A questionof trust: How AI isaddressinggreenwashingconcerns | CFA Institute
- IFC: Malena
- Microsoft: Transforming the energy industry with the power of AI – Microsoft News Center Canada
- ISA: Embracing the Future of Energy Storage with AI-Driven Technologies
- The Guardian: AI-powered personalised medicine could revolutionise healthcare (and no, we’re not putting ChatGPT in charge) | Mihaela van der Schaar | The Guardian
- National library of medicine: Artificial Intelligence in Genetics - PMC
- CNBC: DeepMind solves protein folding ‘grand challenge’ with AlphaFold A.I.
- Microsoft: AI and preventative healthcare: Diagnosis in the blink of an eye - Microsoft Stories Asia
- IAPB: Diabetic Retinopathy - The International Agency for the Prevention of Blindness
- Parametric: 10 Best AI Tools for Urban Planning
- UNU: Artificial Intelligence Can Transform Global Food Security and Climate Action | United Nations University
- BCG: How AI Can Speed-Up Climate Action | BCG
- WEF: China's approach to data and AI is changing. Here's how | World Economic Forum
- South China Morning Post: Tech war: China creates US$8.2 billion AI investment fund amid tightened US trade controls | South China Morning Post
- WIPO: China-Based Inventors Filing Most GenAI Patents, WIPO Data Shows
- WEF: What Is The Social Economy? And How Does It Work? | World Economic Forum
- WEF: AI for social innovation | World Economic Forum
- BloombergNEF: Liebreich: Generative AI – The Power and the Glory | BloombergNEF
- Business Norway: Mature Norwegian data centre industry supports AI explosion
- Arxiv paper. 2304.03271
- MIT: DeepSeek might not be such good news for energy after all | MIT Technology Review
- ITU publications: AI Ready – Analysis Towards a Standardized Readiness Framework
- UN: CDP-excerpt-2023-1.pdf
- IAIS : Public consultation on draft Application Paper on the supervision of artificial intelligence - International Association of Insurance Supervisors
- WEF: WEF_Responsible_AI_Playbook_for_Investors_2024.pdf
- IBM: Why an AI recruiter can be as biased as the humans that built it - The Times & The Sunday Times
- MIT Management: When AI Gets It Wrong: Addressing AI Hallucinations and Bias - MIT Sloan Teaching & Learning Technologies
- Nature: The role of artificial intelligence in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals | Nature Communications
- LSE: Brave New Words: How AI Will Revolutionize Education – review | LSE Review of Books
- ScienceDirect: Enhancing mental health with Artificial Intelligence: Current trends and future prospects - ScienceDirect
- UNDP: The AI Revolution: Is it a Game Changer for Disability Inclusion? | United Nations Development Programme
- National Library of Medicine: Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Management of Drinking Water: A Narrative Review - PMC
- Amazon: Meet five organisations using AI for social good
- AI for good: Eureka - The intelligent assistant for refugees - AI for Good Foundation
Important Legal Information
This document has been prepared by Banco Santander, S.A. ("Santander") for information purposes only and is not intended to be, and should not be construed as, investment advice, a prospectus or other similar information material.
This material contains information compiled from a variety of sources, including business, statistical, marketing, economic and other sources. The information contained in this material may also have been compiled from third parties, and this information may not have been verified by Santander and Santander accepts no responsibility for such information.
Any opinion expressed in this document may differ from or contradict opinions expressed by other members of Santander. The information contained in this material is of a general nature and is provided for illustrative purposes only. It does not relate to any specific jurisdiction and is in no way applicable to specific situations or individuals. The information contained in this document is not an exhaustive and formal analysis of the issues discussed and does not establish an interpretative or value judgement as to their scope, application or feasibility. Although the information contained in this document has been obtained from sources that Santander believes to be reliable, its accuracy or completeness is not guaranteed. Santander assumes no responsibility for the use made of the information contained herein.